Polycystic Ovary Syndrome – PCOS
The panel of italian experts phrased pcos in a webinar on February 3 2020 as:
“Pcos is a well established medical condition that negatively affects reproduction, general health, sexual health and quality of life”
Definition :
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a multifaceted disease with an impact on various aspects of women’s life such as aesthetics, reproduction, metabolism, psychological well being and sexuality.

Etiopathogenesis and prevalence :
Pcos is a very common endocrine and metabolic disorder with a prevalence of 6-15%.Many patients have impaired insulin action, hyperinsulinemia and obesity, therefore genetic and environmental factors play a crucial role in the etiopathogenesis of pcos
It is important to know the various types of a disease for the proper diagnosis.
Types of pcos:
1. Insulin resistant pcos:
Mostcommon type. Smoking, sugar transfat are said to be the causes.
High level of insulin prevents ovulation and triggers ovaries to produce testosterones.
2. Pill induced pcos:
Usually occurs due to birth control pills consumption to suppress ovulatiom
3. Inflammatory pcos:
Occurs due to inflammation hormones get imbalanced and thus ovulation is prevented.
4. Adrenal pcos:
Presents with elevated DHEAS but normal testosterone and androstenedione. Here are the symptoms you have to look for when you suspect pcos.
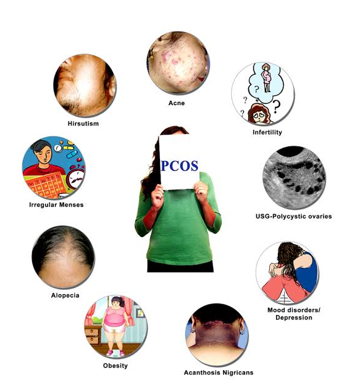
CLINICAL SIGNS :
- Menstrual irregularities(amenorrhea /oligomenorrhea/polymenorrhea)
- Sexual dysfunction
- Eating disorders
- Acne/dark patches in skin
- Inappropriate male features
- Loss of scalp hair
- Oily skin
- Unwanted hair growth
DIAGNOSIS:
Women with pcos shows clinical and biochemical hyperandrogenism, oligoanovulation, micro polycystic morphology of the ovaries.
There are no test to definitively diagnose pcos yet there are test to confirm the above mentioned criteria.
These are as follows:
- Pelvic exam: check for any mass or growth in reproductive organs
- Blood test: blood sugar test and test for hormonal imbalance
- Ultrasound : use to check the appearance of ovaries and the thickness of uterine lining. Transvaginal ultrasound is used.
COMPLICATIONS :
1. High percentage of miscarriages
2. Increased pregnancy
Complications and obsteric and neonatal risks which includes
- Gestational diabetic mellitus
- Pre eclampsia
- Pregnancy induced hypertension
- Post partum hemorrhage and infection
- Preterm delivery
- Still birth
- Operative deliveries

Recent studies shows evidence that proinflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress may directly impact on oocytes quality and may induce endothelial dysfunction thus leading to infertility.
TREATMENT :
- Medication for diabetes mellitus (eg. Metmorphin) helps to manage sugar levels
- Fertility medicaments and assisted reproductive technology
- Progesterone therapy – taking progesterone for 10-14 days every 1-2 months can regulate periods and protect against endometrial cancer.
- Clomiphene-oral anti estrogen
- Letrozole(femara) – it stimulates ovaries and assist in regular ovulation.
- Eflornithine(cream) – slows facial hair growth.
- Lifestyle changes-
1. Maintain healthy weight
2. Limit carb containing food
3. Engage in physical activities.





