What is sexually transmitted diseases??
The term sexually transmitted disease (STD) is used to refer to a condition passed from one person to another through sexual contact. A person can contract an STD by having unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with
someone who has the STD.
Symptoms of STDs in men!!
- Pain or discomfort during sex or urination
- Sores, bumps, or rashes on or around the penis, testicles, anus, buttocks, thighs, or mouth
- Unusual discharge or bleeding from the penis
- Painful or swollen testicles.
Symptoms of STDs in women!!
- Pain or discomfort during sex or urination
- Sores, bumps, or rashes on or around the vagina, anus, buttocks, thighs, or mouth
- Unusual discharge or bleeding from the vagina
- Itchiness in or around the vagina.
Most common STDs
- Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
- Genital Warts and Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
- Genital Herpes (HSV-1, HSV-2)
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases.If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
How Do I Know If I Have HIV?
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too.
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks cells that help the body fight infection, making a person more vulnerable to other infections and diseases.If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
How is HIV transmitted??
HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids that include:
- Blood
- Semen
- Vaginal and rectal fluids
- Breast milk
The virus isn’t transferred in air or water, or through casual contact.

Treatment and complications!!
Untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS within a decade. There’s currently no cure for AIDS, and without treatment, life expectancy after diagnosis is about 3 years. However, treatment with antiretroviral drugs can prevent AIDS from developing.
If AIDS does develop, it means that the immune system is severely compromised, that is, weakened to the point where it can no longer
successfully respond against most diseases and infections.
That makes the person living with AIDS vulnerable to a wide range of illnesses,including:
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Oral thrush, a fungal condition in the mouth or throat
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV), a type of herpes virus
- Cryptococcal meningitis, a fungal condition in the brain
- Toxoplasmosis, a brain condition caused by a parasite
- Cryptosporidiosis, a condition caused by an intestinal parasite
- Cancer, including Kaposi sarcoma (KS) and lymphoma.
Syphilis
A bacterial infection usually spread by sexual contact that starts as a painless sore.
Stages of syphilis!!
Primary syphilis
The primary stage of syphilis occurs about three to four weeks after a person contracts the
bacteria. It begins with a small, round sore called a chancre. A chancre is painless, but it’s highly infectious. This sore may appear wherever the bacteria entered the body, such as on or inside the mouth, genitals, or rectum.
Secondary syphilis
Skin rashes and a sore throat may develop during the second stage of syphilis. The rash won’t itch and is usually found on the palms and soles, but it may occur anywhere on the body. Some people don’t notice the rash before it goes away.
Tertiary syphilis
Tertiary syphilis can occur years or decades after the initial infection. Tertiary syphilis can be life-threatening. Some other potential outcomes of tertiary syphilis include:
- Blindness
- Deafness
- Mental illness
- Memory loss
- Destruction of soft tissue and bone
- Neurological disorders, such as stroke or meningitis
- Heart disease
- Neurosyphilis, which is an infection of the brain or spinal cord.
Treatment and prevention!!
Early treatment with penicillin is important, as the disease can lead to life threatening consequences in the long term.
At a later stage, syphilis remains curable. However, a person may require a longer course of penicillin.
If nerve or organ damage occurs during the later stages of syphilis, treatment will not repair it. Treatment can, however, prevent further damage by clearing the bacteria from a person’s body.
Gonorrhea!!
A sexually transmitted bacterial infection that, if untreated, may cause infertility.
Transmission of Gonorrhea!!

perinatally from mother to baby during childbirth.
Treatment and complications
Adults with gonorrhea are treated with antibiotics. Due to emerging strains of drug- resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the Centersfor
Disease Control and Prevention recommends that uncomplicated gonorrhea be treated with the antibiotic ceftriaxone — given as an injection — with oral azithromycin (Zithromax).
An infection that causes warts in various parts of the body, depending on the strain. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
If left untreated!!
Untreated gonorrhea can lead to major complications, such as:
- Infertility in women. Gonorrhea can spread into the uterus and fallopian tubes, causing pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- Infertility in men. Gonorrhea can cause a small, coiled tube in the rear portion of the testicles where the sperm ducts are located (epididymis) to become inflamed (epididymitis). Untreated epididymitis can
lead to infertility. - Infection that spreads to the joints and other areas of your body.Fever, rash, skin sores, joint pain, swelling and stiffness are possible results.
- Increased risk of HIV/AIDS. Having gonorrhea makes you more susceptible to infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), thevirus that leads to AIDS.
- Complications in babies. Babies who contract gonorrhea from their mothers during birth can develop blindness, sores on the scalp and infections.
Prevention!!
Abstaining from sex is the surest way to prevent gonorrhea. But if you choose to have sex, use a condom during any type of sexual contact, including anal sex, oral sex or vaginal sex. Limit your number of sex partners.
Chlamydia

What causes chlamydia??
- Newborn babies can acquire chlamydia from their mother during birth.
- Sex without a condom and unprotected oral sex are the main ways a chlamydia infection can be transmitted. But penetration doesn’t have to occur to contract it.
- Touching genitals together may transmit the bacteria. It can also be contracted during anal sex.
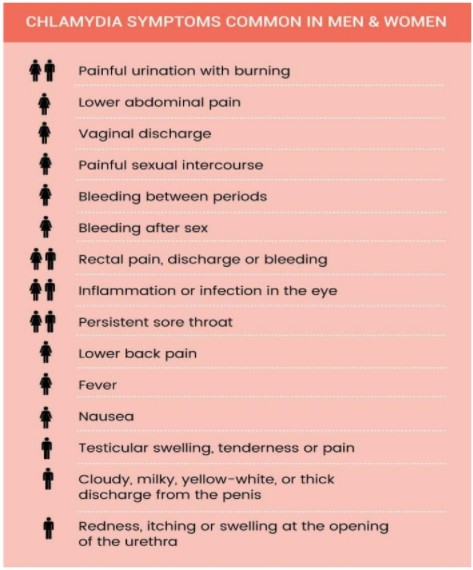
Symptoms in men!!
Some of the most common symptoms of chlamydia in men include:
- Burning sensation during urination
- Yellow or green discharge from the penis
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Pain in the testicles
Symptoms in women!!
Some of the most common symptoms of chlamydia in women include:
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Vaginal discharge
- Burning sensation during urination
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis)
- Bleeding between periods
How to treat??
Chlamydia can be easily treated with a short course of antibiotics. You may be able to take all the antibiotics in one day, or over a week, depending on the type of treatment you are prescribed. It’s important to not have sex until you and your current sexual partner/s have finished treatment. If you’ve had the one-day course of treatment,you should avoid having sex for seven days afterward
HPV:Human papillomavirus
An infection that causes warts in various parts of the body, depending on the strain. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI).
What causes HPV??
- HPV infection occurs when the virus enters your body, usually through a cut, abrasion or small tear in your skin. The virus is transferred primarily by skin-to-skin contact.
- Genital HPV infections are contracted through sexual intercourse, anal sex and other skin- to-skin contact in the genital region. Some HPV infections that result in oral or upper respiratory lesions are contracted through oral sex
- Warts are contagious. They can spread through direct contact with a wart. Warts can also spread when someone touches something that already touched a wart.
What are the symptoms?
A person may have one small skin bump, a cluster of bumps, or stem-like protrusions. These warts can range in size and appearance, and they may be:
- Large or small
- Flat or cauliflower-shaped
- White, pink, red, purplish-brown, or skin-colored
They can form on the:
- Vulva
- Cervix
- Penis or scrotum
- Anus
- Groin area
Treatment and Prevention!!
There’s no cure for the virus and warts may go away on their own. Treatment focuses on removing the warts. A vaccine that prevents the HPV strains most likely to cause genital warts and cervical cancer is recommended for boys and girls.