“You are braver than you believe, stronger than you seem, smarter than you think, and twice as beautiful as you’d ever imagined. Don’t let cancer cause you to sell yourself short or forget your worth.”
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts. After skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United States. Breast cancer can occur in both men and women, but it’s far more common in women.
Lookout for these symptoms!!!

- A breast lump or thickening that feels different fromthe surrounding tissue.
- Change in the size, shape or appearance of a breast.
- Changes to the skin over the breast, such as dimpling
- A newly inverted nipple
- Peeling, scaling, crusting or flaking of the pigmentedarea of skin surrounding the nipple (areola) or breast skin
- Redness or pitting of the skin over your breast, like the skin of an orange
What causes breast cancer??
- When you started having periods: Women who started their periods at an early age (before 12) have a slightly increased risk of breast cancer. The earlier you began your periods, the higher your risk.
- Dense breast tissue: Breast density is the amount of breast tissue compared to fat tissue in your breasts. If you have a high amount of breast tissue compared to fat, you have a ‘high breast density’. This increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Some benign (not cancer) breast conditions: People who have atypical hyperplasia or lobular neoplasia have a slightly increased risk of breast cancer.
- Lifestyle and breast cancer risk: By making small changes and living well now, you can lower your chances of getting breast cancer. It doesn’t guarantee that you won’t develop breast cancer, but leading a healthy lifestyle does give you a better chance.
- Alcohol: Regularly drinking alcohol is associated with a higher risk of developing breast cancer.Limiting the amount of alcohol you drink can reduce your risk of breast cancer.
- Being overweight or obese: Your risk of developing breast cancer increases if you are overweight or obese after the menopause.
- Smoking: There’s growing evidence that smoking slightly increases the risk of breast cancer.The risk is higher in women with a significant family history of breast cancer.
- The pill and HRT: Taking the combined contraceptive pill slightly increases your risk of breast cancer. Within a few years of stopping, however, this risk disappears. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)increases your risk of breast cancer while you’re taking it and for a few years after stopping.
- A family history of breast cancer Having someone in your family with breast cancer doesn’t automatically mean your own risk is increased. For most people, having a relative with breast cancer does not increase their risk.However, a small number of women and men have an increased risk of developing breast cancer because they have a significant family history.
Some myths about breast cancer!!

- If you don’t have a family history of breast cancer,then you won’t get it.
- If you have a healthy lifestyle, you don’t need to worry about getting breast cancer
- Only women get breast cancer
- Breast cancer only affects older women
- A lump on your breast means that you have breast cancer
- Deodorants and antiperspirants cause breast cancer
- A mammogram can cause breast cancer
Stages of breast cancer!!
Stage 0: The cancer has been diagnosed early. It started in the breast ducts or milk glands and has stayed there.
Stage I. Starting at this level, breast cancer is called invasive, meaning it has broken free to attack healthy tissue.
Stage I A:means the cancer has spread into the fatty breast tissue. The tumor itself is no larger than a shelled peanut, or there may be no tumor.
Stage IB means some cancer cells, but just tiny amounts, have been found in a few lymph nodes.
Stage II: The cancer has grown, spread, or both.
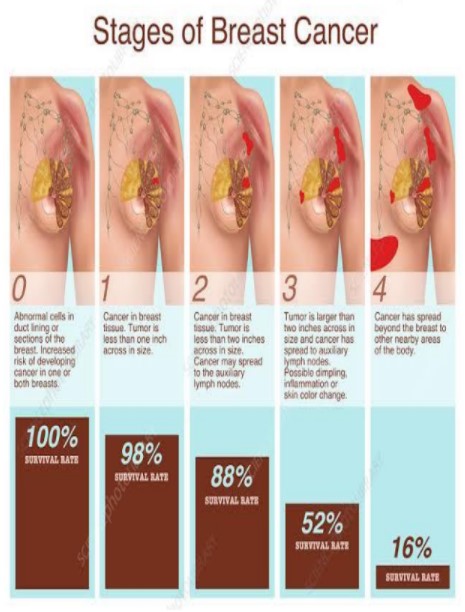
Stage IIA means the tumor in the breast is still small, if there’s one at all. There may be no cancer in the lymph nodes, or it may have spread to as many as three.
stage IIB breast tumor is bigger – it may be the size of a walnut or as big as a lime. It may or may not be in any lymph nodes.
Stage III. The cancer has not spread to bones or organs, but it’s considered advanced, and it’s harder to fight.
Stage IIIA means the cancer has been found in up to nine of the lymph nodes that form a chain from your underarm to your collarbone. Or it has spread to or enlarged the lymph nodes deep in your breast. In some cases there is a large tumor in the breast, but other times there’s no tumor.
Stage IIIA means the cancer has been found in up to nine of the lymph nodes that form a chain from your
underarm to your collarbone. Or it has spread to or enlarged the lymph nodes deep in your breast. In some cases there is a large tumor in the breast, but other times there’s no tumor.
Stage IIIC means cancer has been found in 10 or more lymph nodes, or has spread above or below your collarbone. It’s also IIIC if fewer lymph nodes outside the breast are affected but those inside it are enlarged or cancerous.
Stage IV. Breast cancer cells have spread far away from the breast and lymph nodes right around it. The most common sites are the bones, lungs, liver, and brain.
How to treat???
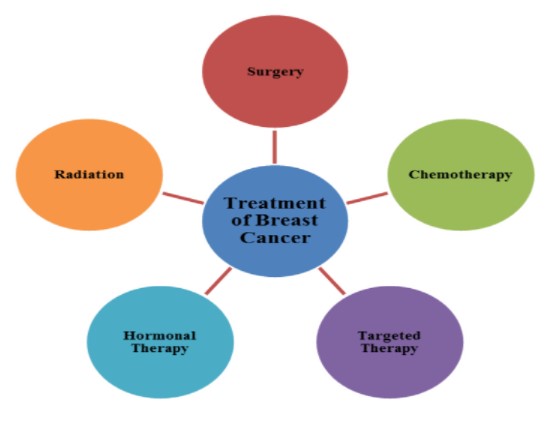
- Surgery: Surgery is the removal of the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue during an operation.Surgery is also used to examine the nearby axillary lymph nodes, which are under the arm.
- Lumpectomy. This is the removal of the tumorand a small, cancer-free margin of healthytissue around the tumor. Most of the breast
remains. - Mastectomy. This is the surgical removal of the entire breast.
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy. In a sentinel lymph node biopsy (also called a sentinel node biopsy or SNB), the surgeon finds and removes 1 to 3 or more lymph nodes from under the arm that receive lymph drainage from the breast.
- Axillary lymph node dissection. In an axillary lymph node dissection, the surgeon removes many lymph nodes from under the arm. These are then examined for cancer cells by a pathologist.
- Reconstructive (plastic) surgery: Women who have a mastectomy or lumpectomy may want to consider breast reconstruction. This is surgery to recreate a breast using either tissue taken from another part of the body or synthetic implants.
- Lumpectomy. This is the removal of the tumorand a small, cancer-free margin of healthytissue around the tumor. Most of the breast
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy x-rays or other particles to destroy cancer cells. A doctor who specializes in giving radiation therapy to treat cancer is called a radiation oncologist. There are several different types of radiation therapy:
- External-beam radiation therapy. This is the most common type of radiation treatment and is given from a machine outside the body. This includes whole breast radiation therapy and partial breast radiation therapy, as well as accelerated breast radiation therapy, which can be several days instead of several weeks.
- Intra-operative radiation therapy. This is when radiation treatment is given using a probe in the operating room.
- Brachytherapy. This type of radiation therapy is given by placing radioactive sources into the tumor.
- Hormonal therapy also called endocrine therapy, is an effective treatment for most tumors that test positive for either estrogen or progesterone receptors (called ER positive or PR positive). This type of tumor uses hormones to fuel its growth. Blocking the hormones can help prevent a cancer recurrence and death from breast cancer when hormonal therapy is used either by itself or after chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapy: is a treatment that targets the cancer’s specific genes, proteins, or the tissue environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival. These treatments are very focused and work differently than chemotherapy. This type of treatment blocks the growth and spread of cancer cells and limits damage to healthy cells.
- Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. You take the medicines as pills or through an IV. Most people get it after surgery to kill any cancer cells left behind. Doctors also prescribe it before surgery to make tumors smaller. Chemo works well against
cancer, but it also can harm healthy cells.






